The Indian Peer-to-Peer Lending Ecosystem – Growth, Regulation & Strategic Roadmap 🇮🇳💸

Understanding the Regulatory Framework: NBFC-P2P Classification 🏛️📜
The RBI’s formal classification of P2P lending platforms as Non-Banking Financial Companies – Peer-to-Peer (NBFC-P2P) has been a game-changer. By recognizing these platforms as regulated financial institutions rather than mere technology intermediaries, the RBI has instilled credibility and trust, both critical for attracting retail and institutional capital.
An NBFC-P2P is essentially a financial intermediary, enabling loans between borrowers and lenders through online mediums, while ensuring compliance with regulatory safeguards. This includes obtaining a Certificate of Registration (CoR) from the RBI before operating legally. Leading players such as Faircent, Finzy, and LenDenClub exemplify this structured approach, showcasing how regulation and technology can coalesce to create scalable financial solutions. ✅
The regulatory backbone ensures platforms adhere to systemic risk management, transparency, and investor protection, all of which are prerequisites for fostering long-term stability in the sector. Without these frameworks, the rapid growth witnessed in P2P lending could expose participants to fraud, default, and operational vulnerabilities, which the RBI’s guidelines are explicitly designed to mitigate. 🛡️

Market Trajectory and Growth Dynamics 📈🌍
India’s P2P lending market is riding a remarkable growth trajectory, fueled by structural gaps in traditional credit delivery and a digitally empowered population. The surge in unsecured consumer and retail loans during fiscal years like 2024 has underscored the appetite for alternative lending mechanisms.
P2P platforms are filling a critical credit accessibility gap, especially for underserved populations and SMEs. Traditional banks, constrained by high operational costs, risk-averse lending models, and bureaucratic friction, often fail to serve these segments efficiently. P2P platforms, in contrast, leverage technology-driven credit assessment, flexible risk pricing, and rapid disbursal mechanisms, delivering loans where banks cannot. This is especially transformative in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, where access to conventional banking remains limited. 🌆💳
The growth is further catalyzed by India’s digitally literate younger population, increasing financial literacy, and expanding participation from individual investors seeking higher returns. Platforms often offer annual yields of up to 15%, significantly outperforming traditional instruments like fixed deposits or savings accounts. This dual benefit credit for borrowers and returns for lenders is the engine driving P2P adoption across the country. 🚀💰

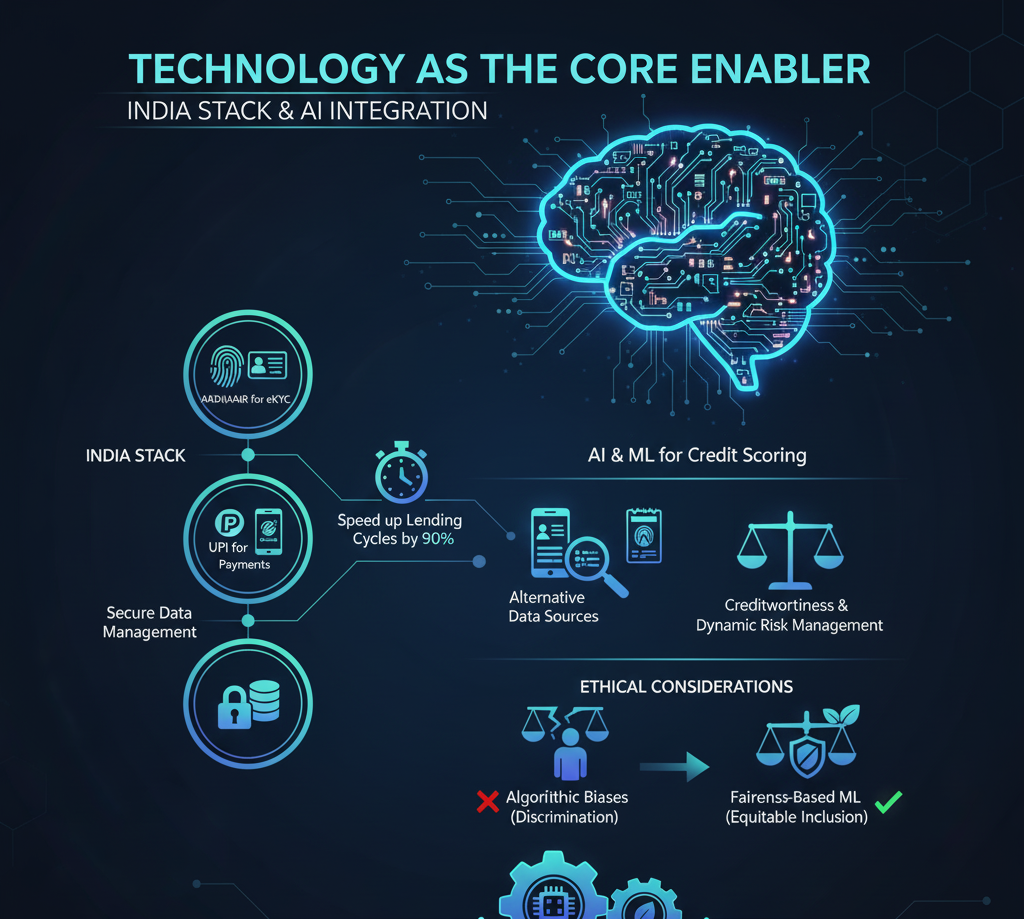
Technology as the Core Enabler: India Stack & AI Integration 🤖💡
India’s P2P sector owes much of its scalability and efficiency to the India Stack, the nation’s digital public infrastructure. This framework includes Aadhaar for eKYC, UPI for payments, and secure data management protocols, which collectively reduce operational costs and speed up lending cycles by up to 90%. 🏎️
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have revolutionized credit scoring, particularly for borrowers without traditional credit histories. By utilizing alternative data sources such as mobile transactions, utility payments, and digital footprints, P2P platforms can assess creditworthiness with unprecedented accuracy. This approach not only enhances inclusion but also ensures dynamic risk management, allowing lenders to make informed decisions.
However, the deployment of AI comes with ethical considerations. Algorithmic biases if unaddressed can perpetuate discrimination based on gender, caste, or geography. Leading platforms are now integrating fairness-based ML solutions, ensuring that financial inclusion is both equitable and sustainable. 🌱⚖️
Investor Protection and Risk Mitigation 🛡️📊
While growth is robust, the NBFC-P2P sector is not without risk. Fraud, operational lapses, and macroeconomic fluctuations pose significant challenges. Recognizing this, the RBI has introduced updated capital exposure limits and net worth certifications to safeguard both retail and institutional investors.
Aggregate exposure cap: ₹50 Lakh per lender across all P2P platforms.
Net worth verification: Lenders with exposure above ₹10 Lakh must certify a minimum net worth of ₹50 Lakh via a Chartered Accountant.
These measures professionalize the sector, ensuring that high-volume lenders are financially sound while maintaining systemic stability. Platforms complement this with risk-based pricing systems and fraud detection mechanisms, creating a secure ecosystem that balances high returns with responsible lending.


Competitive Landscape and Strategic Differentiation 🏆🌟
The Indian P2P market is highly competitive, with platforms differentiating themselves via technology, risk management, and niche focus.
Faircent: Stability and high on-time repayment rates (99%), tech-enabled risk mitigation.
LenDenClub: Quick disbursals, high returns up to 15%, low investment minimums.
Finzy: Personalized lending options, rigorous credit assessment, and dynamic risk pricing.
Some platforms like IndiaP2P focus on impact-driven lending, targeting SMEs, women-led enterprises, and rural borrowers. This strategic alignment with social impact goals not only supports financial inclusion but also attracts impact-conscious investors, creating a virtuous cycle of profitability and social good. 🌍💖
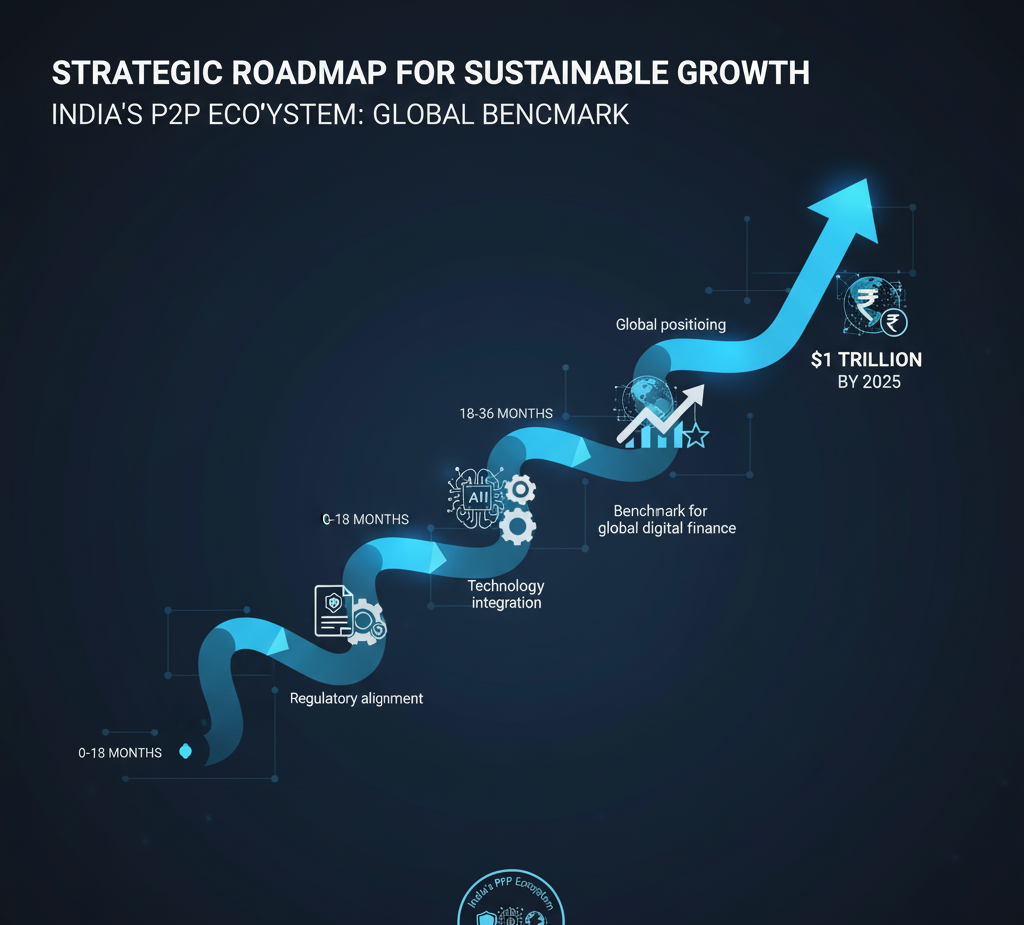
Strategic Roadmap for Sustainable Growth 🛤️📌
The roadmap for the next 5 years emphasizes regulatory alignment, technology integration, and global positioning.
By strategically leveraging technology, ethical AI, and regulatory compliance, India’s P2P ecosystem is on track to become a benchmark for global digital finance. 🌐💹
Focus on regulatory compliance, advanced fraud deterrence, and ethical AI implementation. Automated supervisory reporting ensures alignment with RBI directions, strengthening systemic transparency.
Expand to Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, diversify products (MSME loans, green finance, education loans), and pursue co-lending partnerships with large financial institutions.
Establish the sector as a globally recognized institutional asset class, integrate Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) for lower transaction costs, and advocate for advanced risk hedging tools to manage macroeconomic fluctuations.

Conclusion: India’s P2P Lending
A High-Growth, Responsible Future 🚀🇮🇳
India’s P2P lending sector exemplifies the intersection of technology, regulation, and inclusion. Leveraging India Stack, AI-driven risk assessment, and proactive RBI oversight, platforms are not only bridging critical credit gaps but also creating attractive, secure investment opportunities.
For platform operators, the priority remains strict regulatory adherence, robust risk management, and ethical AI deployment. Institutional investors should focus on platforms with proven repayment records, risk-based pricing, and scalable co-lending models. Those aligning commercial gains with social impact are poised to emerge as sector leaders, demonstrating that profitability and inclusion can coexist. 💡🌱
The Indian P2P landscape is dynamic, innovative, and poised for long-term growth. Its success story offers valuable lessons for global financial markets, showing how technology and regulation can converge to create a responsible, high-performing digital credit ecosystem.